
What is Perfusion Index?

Normal pulse oximeter readings usually range from 95 to 100 percent. Values under 90 percent are considered low. Hypoxemia is a below-normal level of oxygen in your blood, specifically in the arteries. Hypoxemia is a sign of a problem related to breathing or circulation, and may result in various symptoms, such as shortness of breath. Normal readings are typically lower for people who live significantly above sea level. Other factors can also interfere with how well a pulse oximeter works, says Georgine Nanos, M.D., a family. So, what is the normal pulse oximeter reading? Typically, blood oxygen saturation level should be at least 89 percent. Most healthy people have a blood oxygen saturation level of 95 and 97 percent. Oxygen concentration level of 92 percent of below can indicate a potential for hypoxemia, an oxygen deficiency in the tissues. Normal pulse oximeter readings range from 95 to 98% for an adult. If you see 92 or less, it’s time to make an appointment. You can google “pulse oximeter readings normal chart” for details. Oximeters work by searching for oxygen-carrying hemoglobin molecules with the help of light waves that it emits. If you do have a pulse oximeter and are checking your oxygen levels, it’s important to know that a level between 95 and 97% is considered normal by the American Lung Association; anything below that would be a reason to call a doctor, and anything under 90% would be a reason to go to the emergency room.
Perfusion Index, or PI, is the ratio of the pulsatile blood flow to the non-pulsatile static blood flow in a patient’s peripheral tissue such as in a fingertip, toe, or ear lobe. Perfusion index is an indication of the pulse strength at the sensor site. The PI’s values range from 0.02% for very weak pulse to 20% for extremely strong pulse.
The perfusion index varies depending on patients, physiological conditions, and monitoring sites. Because of this variability, each patient should establish his own “normal” perfusion index for a given location and use this for monitoring purposes.
In neonatal acute care, a low PI is an objective and accurate measure of acute illness. It is superior to qualitative approach such as foot warmth.
Perfusion Index is also used as an early warning of anesthetic failure. Studies have shown that an increase in PI is an early indicator that general or epidural anesthesia has initiated peripheral blood vessel dilation, which typically occurs before the onset of anesthesia. Lacking the spike would indicate the lack of anesthetic effect.
Oximeter Normal Range
The perfusion index trend can give the care provider extra information about the patient.
- The waveform can depict irregular heartbeat.
- A weak waveform can indicate incorrect placement of the oximeter or a dirty LED sensor.
- PI% can indicate strength of pulse and also indicate effects of anesthesia (a spike indicates initial anesthetic affect).
Pulse Oximeter Pleth (Plethysmograph)
The change in blood volume can be detected in peripheral parts of the body such as the fingertip or ear lobe using a technique called photoplethysmography. It can measure the change in the volume of arterial blood with each pulse beat. The pulse oximeter that detects the signal is called a plethysmograph (or ‘Pleth’ for short).
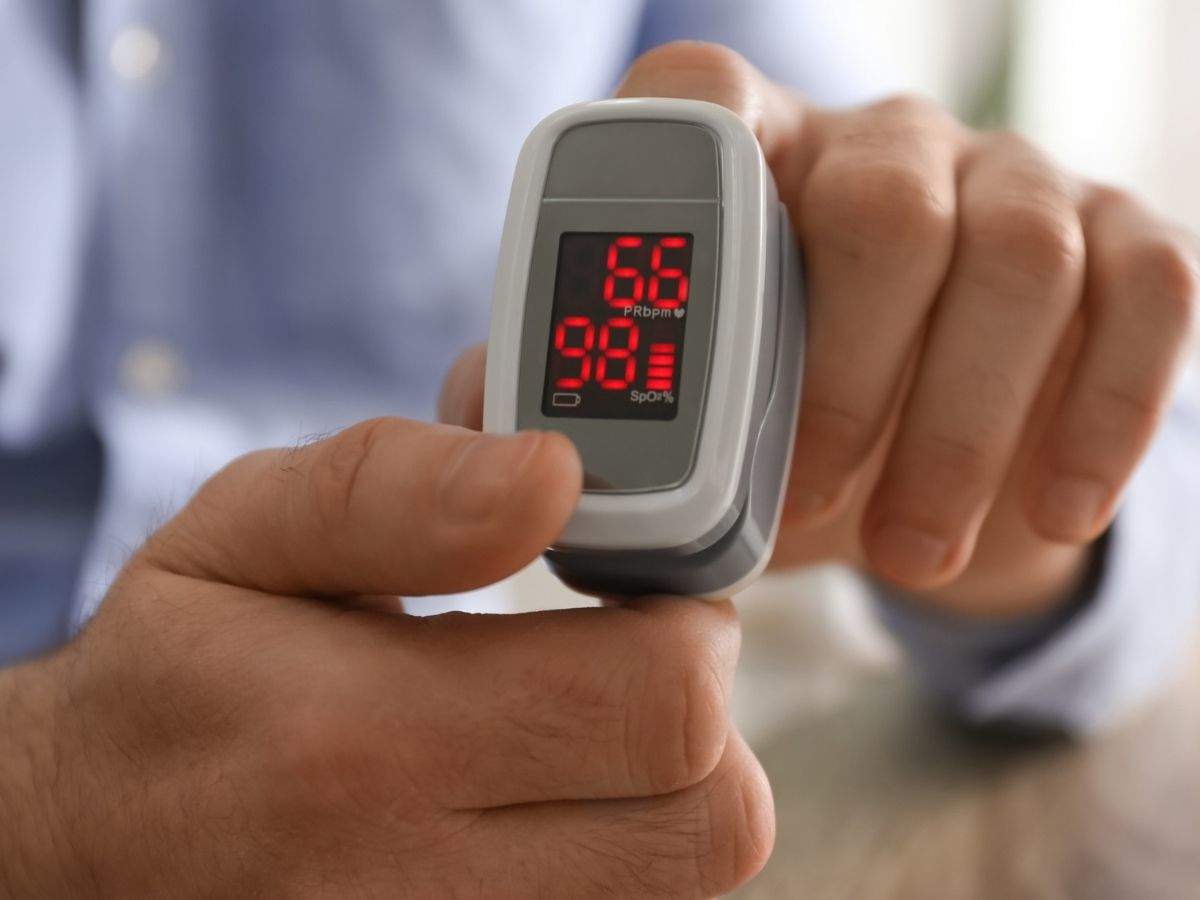

Heart Rhythm
Pleth is useful to detect irregular heart rhythm. The primary function of the heart is to supply blood and nutrients to the body. The regular beating, or contraction, of the heart moves the blood throughout the body. By watching the pleth waveform, the heart beating pattern is clearly displayed. When a heart patient is having discomfort, it is important to observe the pleth waveform and relate the information to his doctor. Since the discomfort is generally transient, a doctor may not be able to see the waveform during an office visit.
Signal Strength
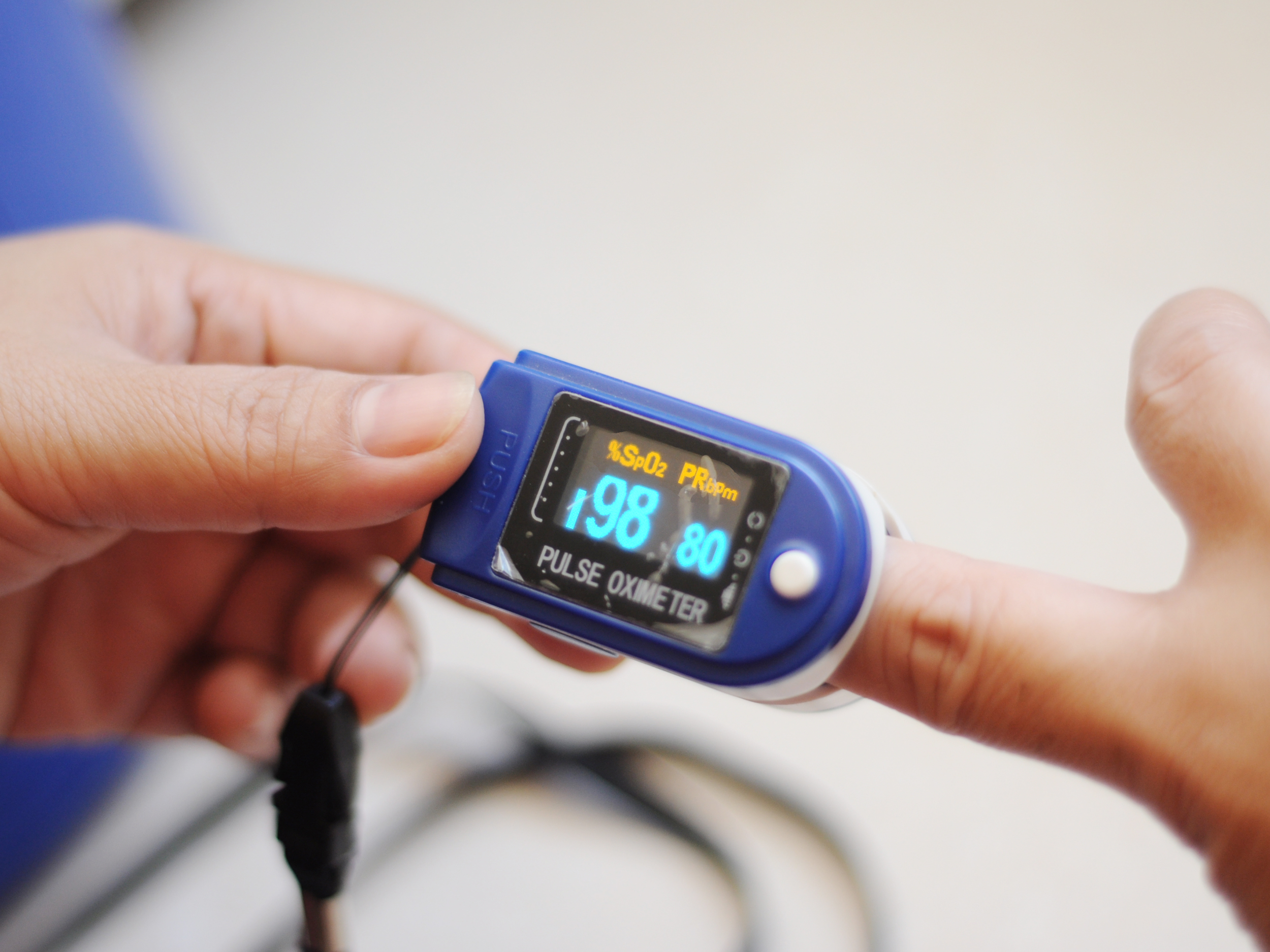
Weak signal is indicated by the amplitude of the waveform. If the signal is too low, it would affect the accuracy and functioning of the pulse oximeter. If your oximeter is not giving the correct result, check if the signal strength is too low.
There can be several causes for a weak signal:
- Low blood perfusion
- Dirty sensors or LED lights
- Improper positioning of the oximeter
- Low blood perfusion can also be caused by cold temperatures and the person’s general health.
TO DOWNLOAD A PDF OF THIS ARTICLE, CLICK HERE.
©Hopkins Medical Products 2020

Perfusion Index with Trend Options
Hopkins Medical Products carries several pulse oximeters with PI percentage and waveform trend capabilities. Check out our unique selection below.
Hopkins Fingertip Oximeter with Perfusion Index
(#594027)
HMP Pediatric Fingertip Pulse Oximeter
(#594023)
Oximeter Normal Readings
Hopkins Wave Plus Fingertip Pulse Oximeter
(#HM594030-BK)
