How many unpaired electrons are in a N atom?
Nitrogen is the seventh element with a total of 7 electrons. In writing the electron configuration for nitrogen the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for N goes in the 2s orbital. The remaining three electrons will go in the 2p orbital. Well, nitrogen's atomic number is 7, so it has 5 valence electrons (two in the 2s orbital and three in the 2p orbitals) and 2 core electrons (two in the 1s orbital). For simple atoms, filling electrons goes in accordance with: The Aufbau principle (lowest to highest energy ordering). The atomic number of the nitrogen is seven, which makes its electronic configuration 1s2 2s2 2p3. As the p shell needs to accommodate a maximum of six electrons, there is a scarcity of three electrons. It makes a single nitrogen atom to have five valence electrons. Nitrogen thirteen. So thirteen minus seven gives us six. Therefore, there are six neutrons in nitrogen. Thirteen the number of electrons. If we're talking about neutral species which we are in this compound that was given to us or in this Adam nitrogen, therefore on Lee has seven electrons to balance the number of protons, making it a neutral Adam. In this video we'll assign formal charge to nitrogen and just to remind you of the definition for formal charge formal charge is equal to the number of valence electrons in the free atom minus the number of valence electrons in the bonded atom or another way of saying that formal charge is equal to the number of valence electrons the atom is supposed to have minus the number of valence.
1 Answer
Well, nitrogen's atomic number is
For simple atoms, filling electrons goes in accordance with:
- The Aufbau principle (lowest to highest energy ordering)
- Hund's rule (one electron per orbital first, then pair them up after all orbitals for a single energy level are singly occupied)
- The Pauli Exclusion Principle (opposite spins on the two electrons in each orbital, if there are two; otherwise spin up is the common convention).
Thus, the orbital configuration is (energy increases as you go upwards on this scale):
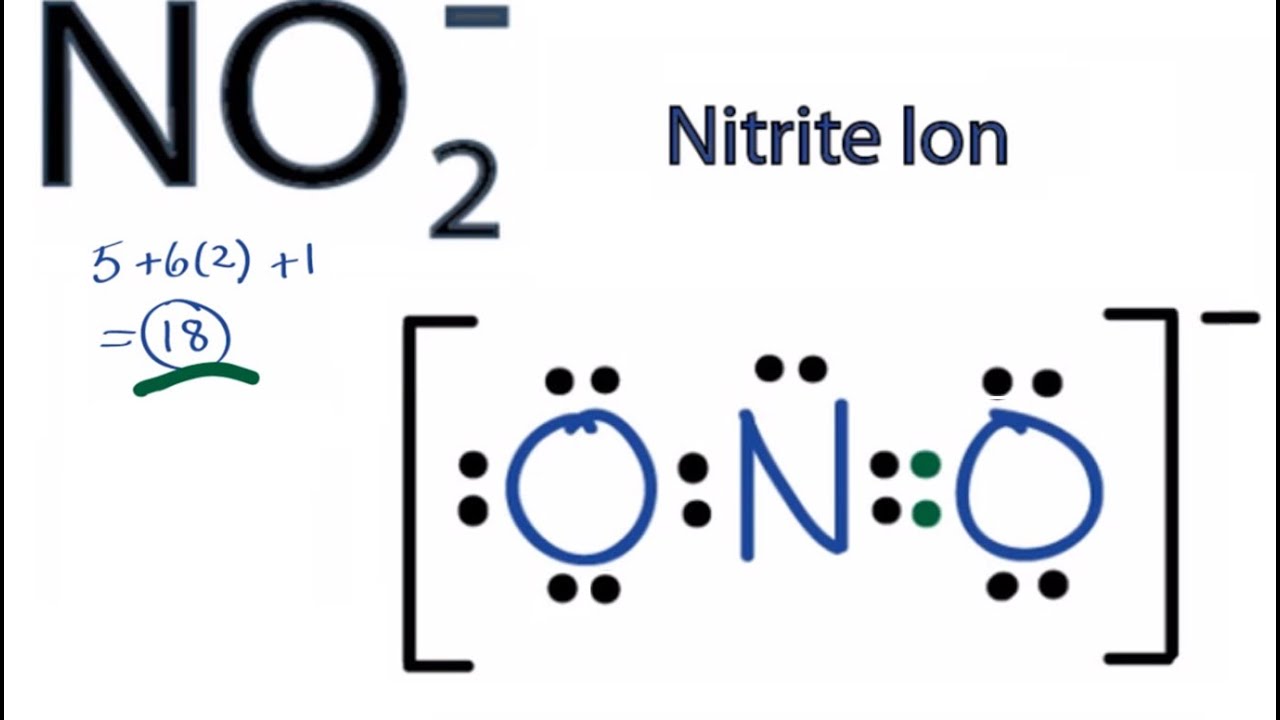
Based on this diagram, how many electrons are unpaired?
Related questions
This element has 7 protons, 7 electrons and 7 neutrons.
Number Of Electrons In Nitrogen 15
Explanation:
There are 3 subatomic particles present in an atom. They are: protons, electrons and neutrons.
Protons: They carry positive charger and are present in nucleus.Electrons: They carry negative charge and are present around the nucleus.Neutrons: They dos not carry any charge and are present in nucleus.Atomic number is defined as the number of protons or electrons that are present in a neutral atom.
Atomic number = number of protons = number of electrons
Mass number is defined as the sum of number of protons and neutrons that are present in an atom.
Mass number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
Atomic mass is the sum of masses of each isotope each multiplied by their natural fractional abundance. This is also related to protons and neutrons present in an atom.
We are given:
An element having formula
Atomic number = Number of electrons = Number of protons = 7
Mass number = 14
Number of neutrons = 14 - 7 = 7
Atomic mass of nitrogen = 14.01 amu
Hence, the given element has 7 protons, 7 electrons and 7 neutrons.
Atomic number = number of electrons = number of protons
We get to know the atomic number of Nitrogen as 7 from the periodic table.
So Nitrogen contains 7 protons and 7 electrons.
To find the number of neutrons we make use of the formula
Mass number - atomic number = number of neutrons
So number of neutrons in a Nitrogen atom =14-7=7 neutrons.
Atomic mass of Nitrogen is 14.0067 amu.
Average Atomic mass is the sum of the atomic mass of the isotopes multiplied by the abundance
Thats why we get a fractional number as atomic mass.
If suppose an element has 3 isotopes then,
Average atomic mass
Is the formula to find the average atomic mass of an element.
So the Answer is Nitrogen atom has 7, protons 7, electrons and 7 neutron

Explanation:
To describe an atom of N-14, one must know the subatomic particles composed in it.
An atom is considered as the smallest particle that takes part in a chemical reaction. In an atom, the subatomic particles are the protons, neutrons and electrons.
The protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus at the center of the atom. These particles are the most massive in an atom and they determine the mass of the atom. The mass number of an atom is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons.
The extra-nuclear space is occupied by electrons. Electrons have little to no mass but the occupy the bulk volume in an atom. These particles are negatively charged.
In a neutral atom of N-14, we know for sure that the atom has not lost or gained electrons.
Number Of Electrons In Nitrogen Ion
We can identify that N-14 is a nitrogen atom with a mass number of 14.

The periodic table arranges elements based on their atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons. The number of protons in nitrogen is 7 based on the periodic table of elements. Due to the neutral nature of the atom, the number of protons and electrons are the same. Therefore, the atom has 7 electrons.
Since the mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons
number of neutrons = mass number - number of protons
number of neutrons = 14 - 7 = 7
The protons are positively charged particles and neutrons carry no charges.
(b) The atomic number of strontium (listed inside the front cover) is 38. Thus, all atoms of this element have 38 protons and 38 electrons. The strontium-90 isotope has 90 – 38 = 52 neutrons. Magnesium has three isotopes, with mass numbers 24, 25, and 26.
Explanation:
Number Of Electrons In Nitrogen Is 7 What Is Its Valency

Number Of Electrons In Nitrogen Atom
